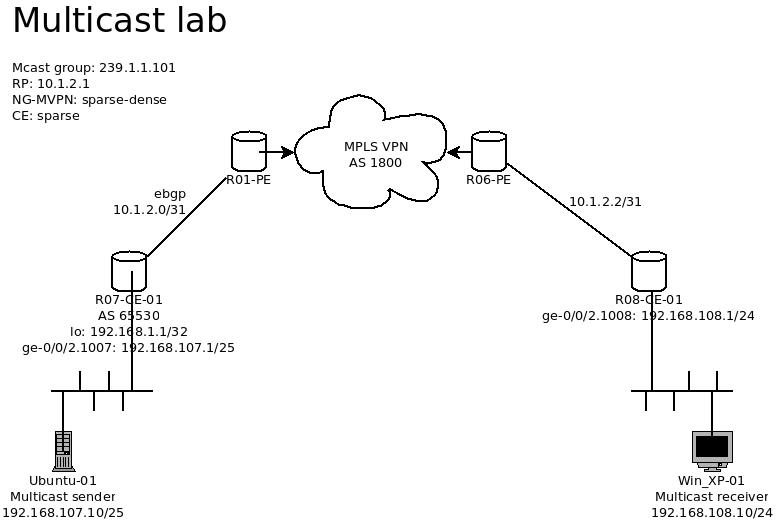
It sure has been some times since the last multicast post. This time, we will put the lab into a higher level, and will be running the multicast on the MPLS VPN platform. Since this post is focusing on MCast only, the configuration for MPLS network will not be described with my detail. So let s dig in.
(!!! the following configuration is built on top of the MPLS VPN.)
(!!! the following configuration is the minimum configuration for NG-MVPN only.)
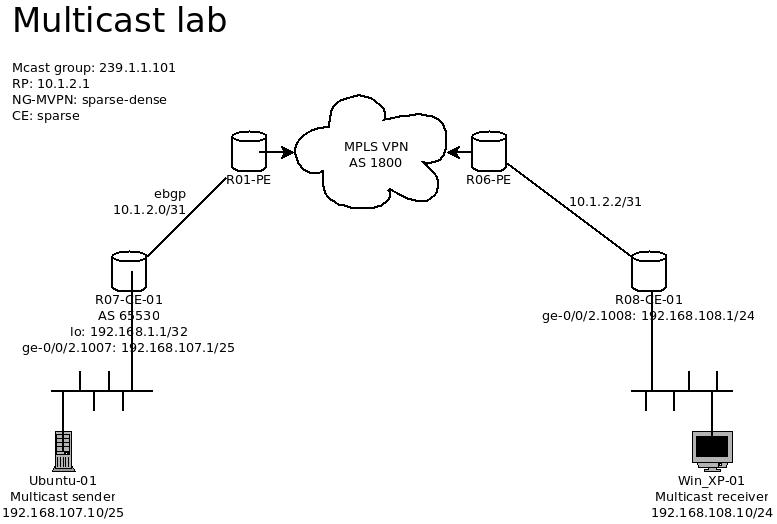
This lab has is running the MCast traffic on the MPLS VPN network, and the feature of NG-MVPN will be using as the method for passing the MCast traffic within a single VRF.
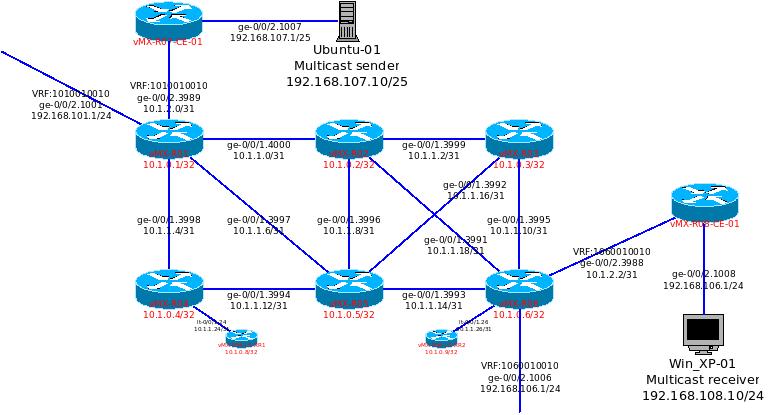
The detail of the MPLS network is shows as below with the IP addresses listed.
– The RP IP is set to 10.1.2.1, which is the R07-CE-01 router s WAN IP address.
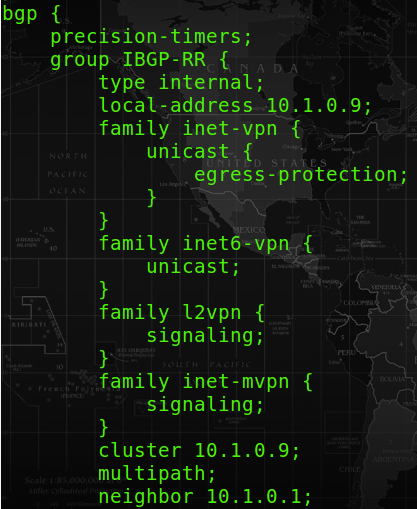
The configuration for setting up a NG-MVPN is required at “Router reflectors” and “PE routers that need to run NG-MVPN with”.
At the route reflector, apply “family inet-mvpn”
At R06-PE (and R01-PE), there will be 2 parts to configure. The first part would be the “family inet-mvpn” at protocol bgp section.
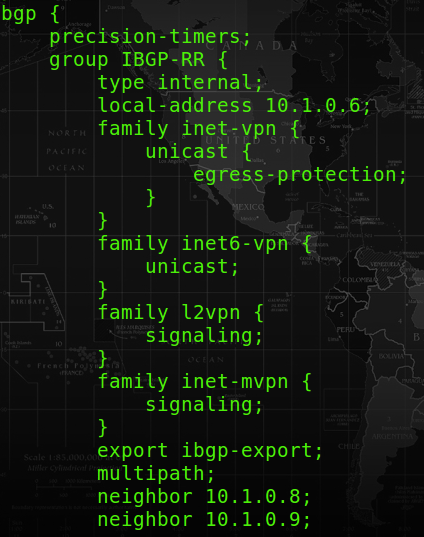
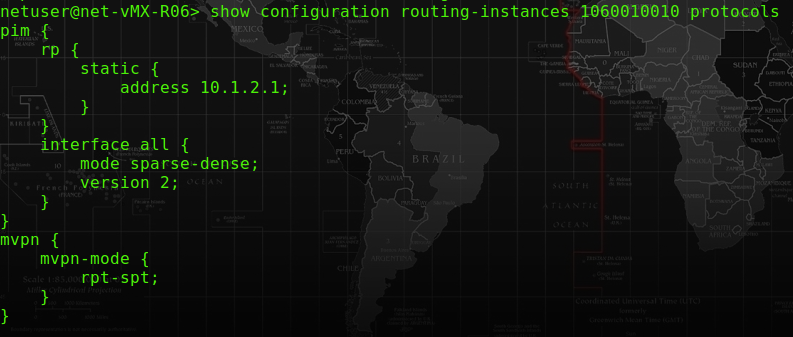
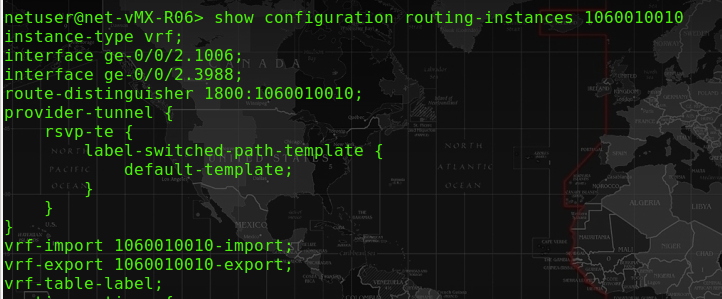
The second part of configurations would be at the VRF of R06-PE, and they are the pim and mvpn and provider-tunnel configuartion.
– The pim configuration is to enable the multicast routing under the VRF.- The mvpn is to enable the multicast vpn feature for the VRF.
– The provider-tunnel is also required for NG-MVPN since NG-MVPN uses RSVP to handle MCast traffic across the MPLS VPN network.
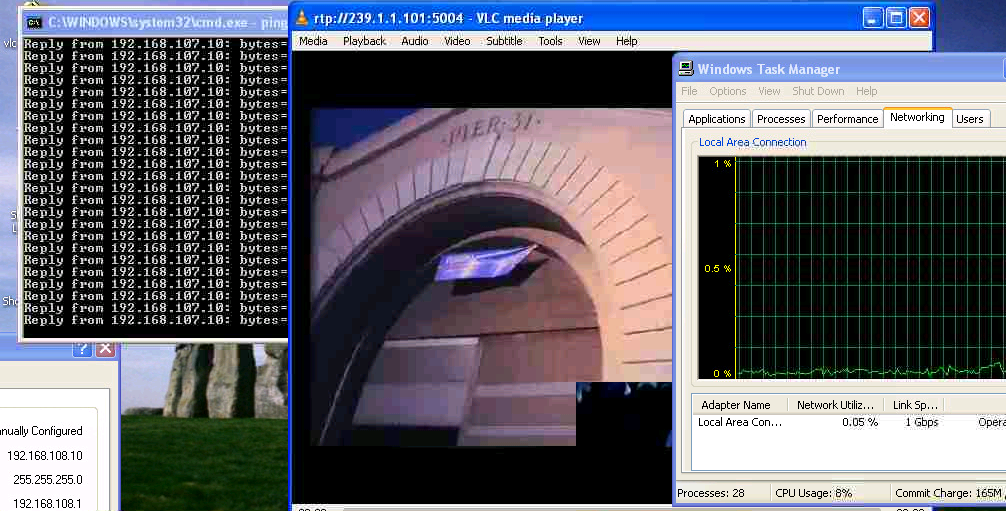
Final result:
MCast video playing on VLC at XP:
– the IP address of Win XP is 192.168.108.1
– able to ping 192.168.107.10 (Streaming server)
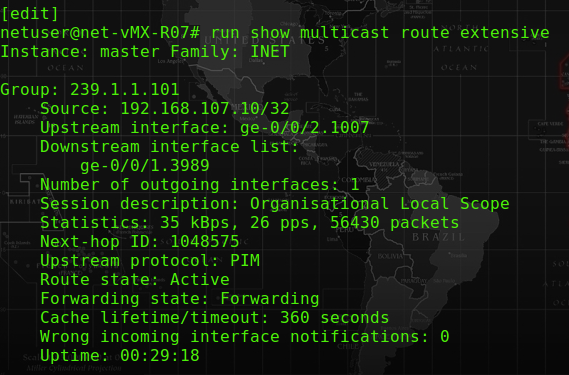
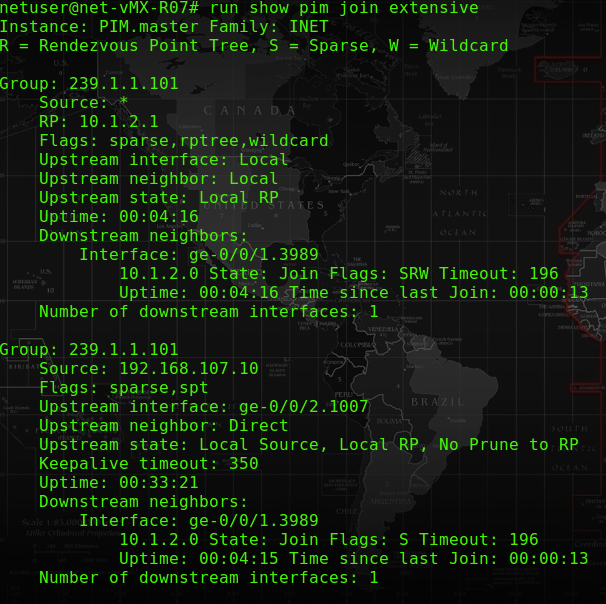
From the CE R07 router, it shows the upstream interface is sending from the Streaming server via ge-0/0/2.1007, and passing the interface via ge-0/0/1.3989.
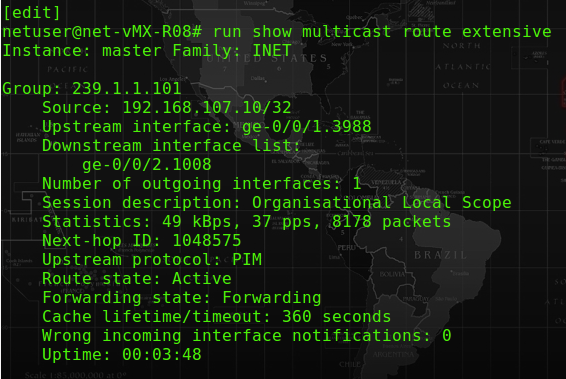
A successful receiving side of R08-CE router should have the following outcome:
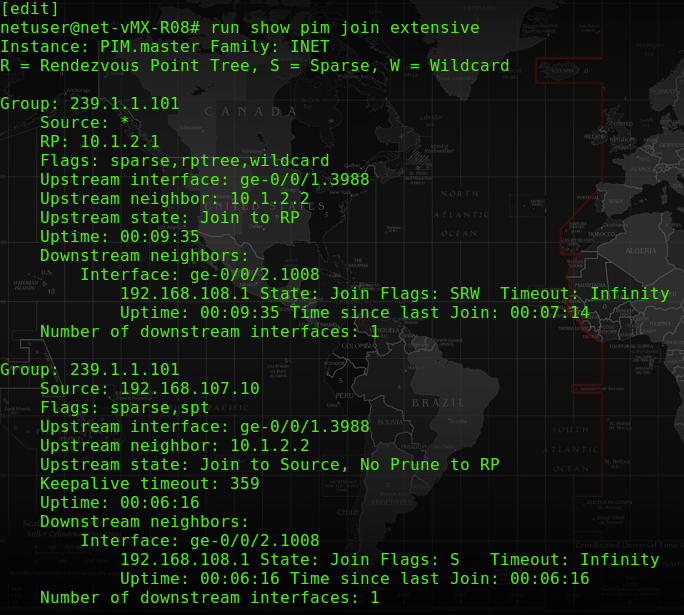
At the PE router that is connecting to MCast sending side CE router, it shows the upstream interface is from ge-0/0/2.3989 and pass to ge-0/0/1.4000 as down stream interface, which pass to another PE router.
– The forwarding state is “Forwarding”.
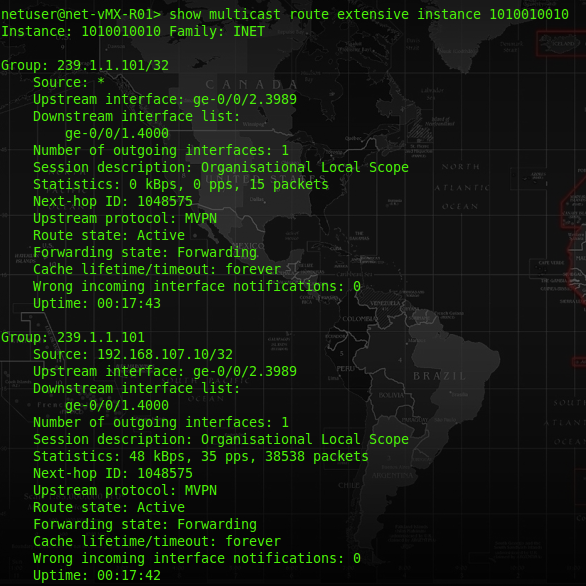
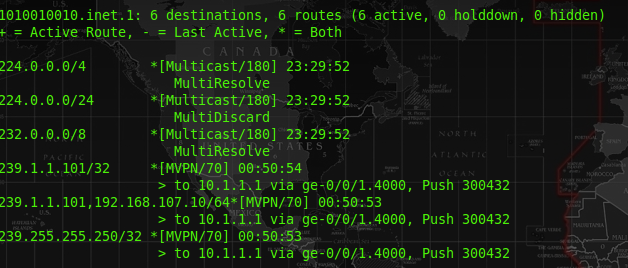
At the route table of R01-PE router, there should be a type 7 route in order to pass the MCast traffic within the VRF.
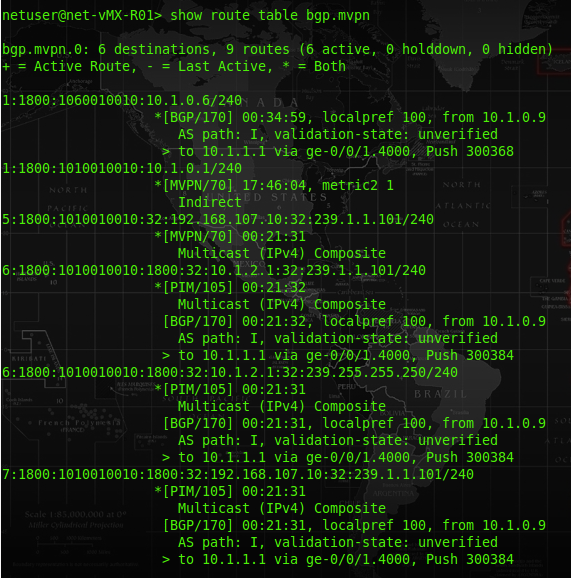
Since NG-MVPN is using RSVP, we could see alot of output and checking would have the term RSVP below. Using the following command to show the MVPN neighbour. In our lab, the MVPN neighbor of vMX-01-PE is 10.1.0.6, which is the vMX-06-PE.
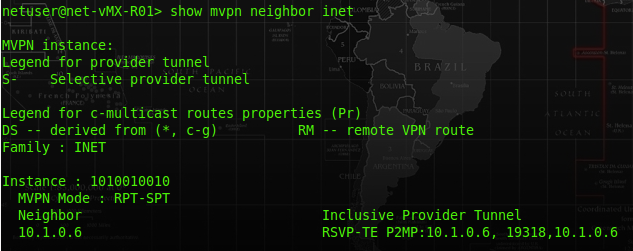
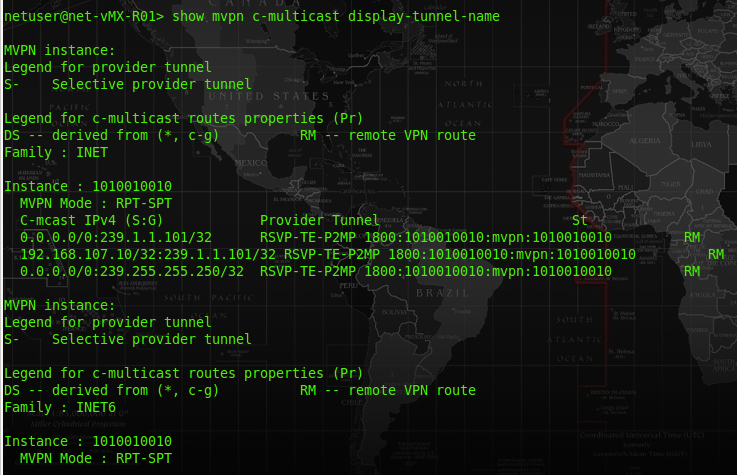
At R01-PE, the route table of VRF 1010010010 should have a route entry for the MCast group ip address, and it will push a label of 300432 for that traffic.
The R01-PE is the ingress router for transferring the MCast traffic, therefore, we can see an entry of “10.1.0.1 (R01-PE) ” to “10.1.0.6 (P06-PE)” at the rsvp session output. This rsvp session is using the label 300432, which we can use this to ensure the VRF 10101010 to using this session to transfer the MCast traffic.
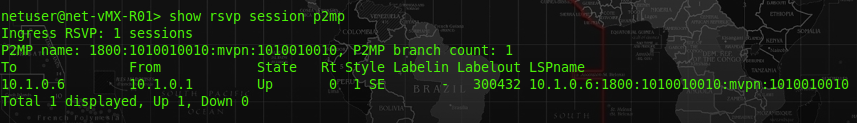
The rsvp session output at R02-PE would show that the session of NG-MVPN is at the “transit”, because this router is in the middle of both ingress (10.1.0.1) and egress (10.1.0.6) router and to pass the MCast traffic only. The below message also shows the packet with label 30432 will be swap with a label 16. It is proved at the 2nd figure below.
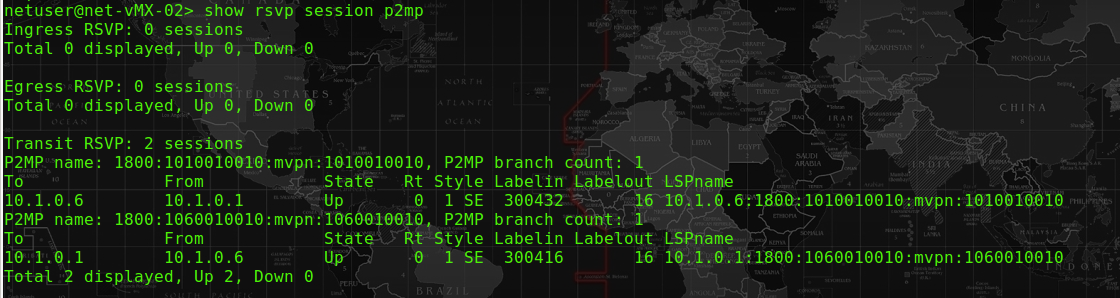
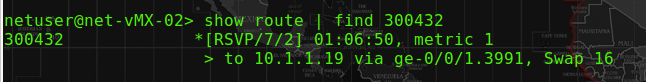
At P06-PE, the session for R01 toR06 is at the egress section, since the R02-PE has swap the label to 16, P06-PE will pass this label 16 packet into the 1060010010 (the VRF).
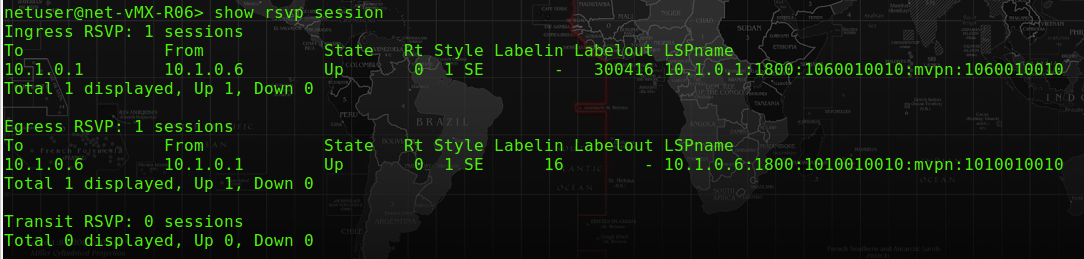
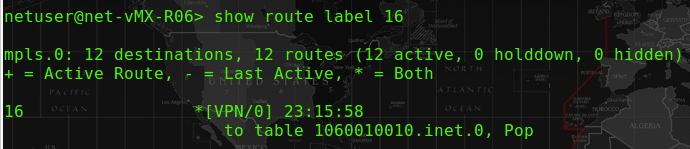
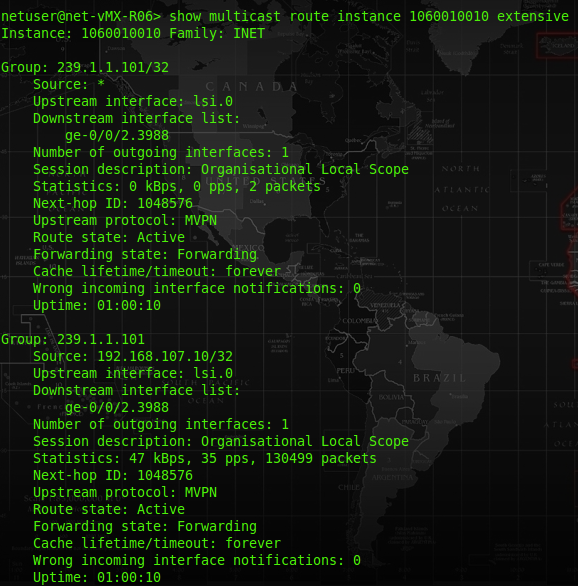
At R06-PE, we could see the MCast traffic for 239.1.1.101 is sending from source 192.168.107.10. The upstream interface unlike the regular interface, it is using “lsi.0” for our case. We could also see some traffic is passing through at the “statistics”.
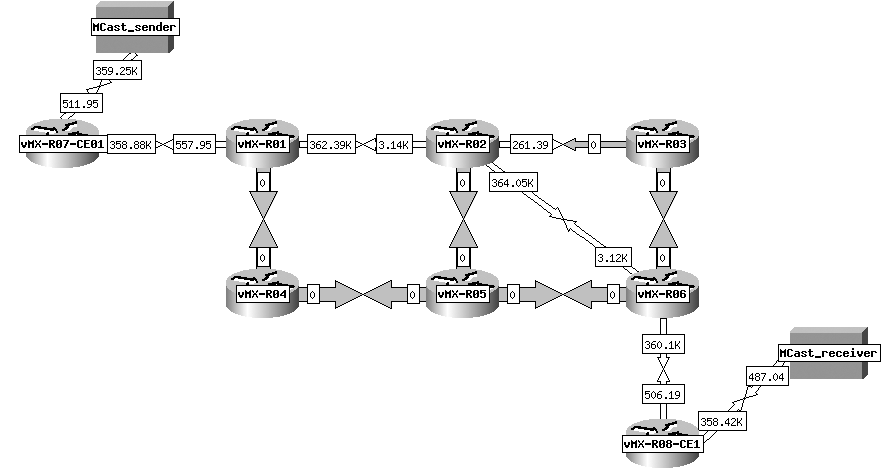
From the cacti weathermap report, the multicast traffic in this case is around 359kbps, which match with the statistics 47KBps (47KBps x 8 = 386kbps) above.
Hi, what version of code is the vMX?
Sorry for the late reply as i barely have time to deal with this blog lately. The vMX version would be 14.1R1. It was from 3 to 4 years ago. There are some newer version available from Juniper s website.